Are you wondering about the purpose of the AppData folder? If so, here's what you need to know.
On Windows 11 (and 10), the system includes an "AppData" folder for each user account that houses three other folders, including the "Local," "LocalLow," and "Roaming," and in this guide, I will explain their purpose and how to access them if you have to troubleshoot specific problems.
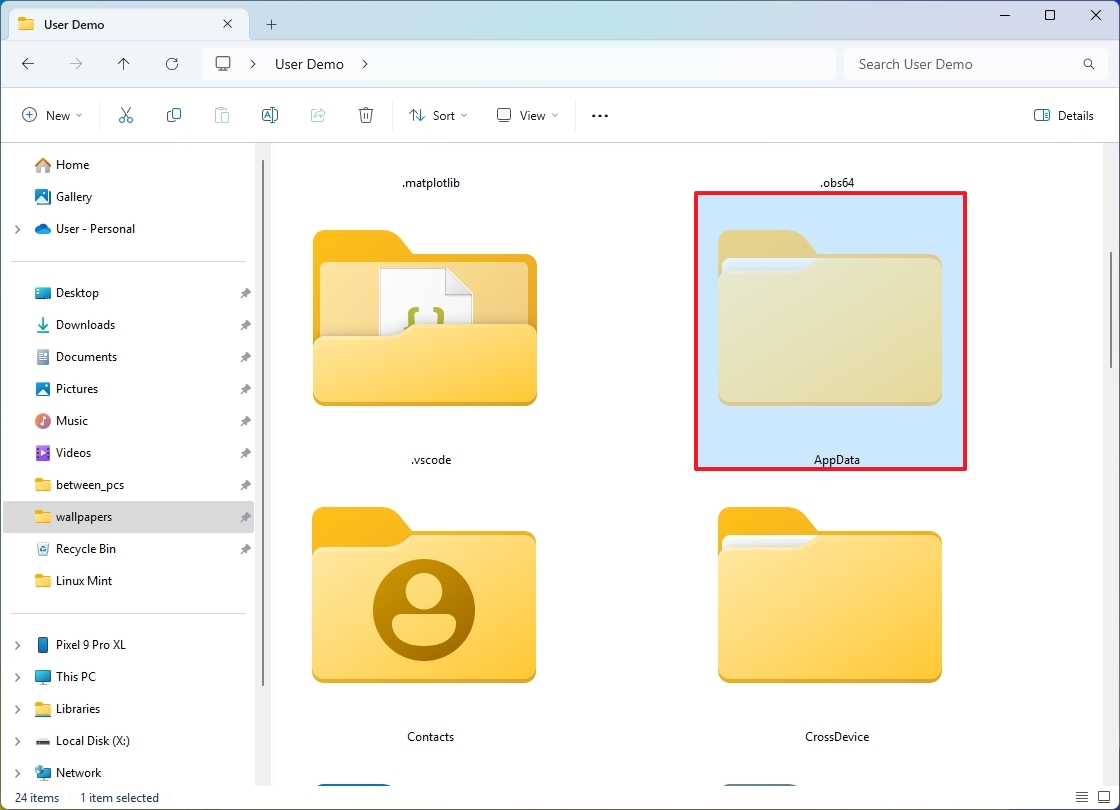
What's the AppData folder on Windows?
The "AppData" (Application Data) folder is a hidden container that stores specific data for your applications (such as cache files, preferences, settings, and other information) so they function correctly.
In other words, it's the central location for apps to store and retrieve data without affecting the application core files and allows each user to configure and customize applications differently.
(Image credit: Mauro Huculak)
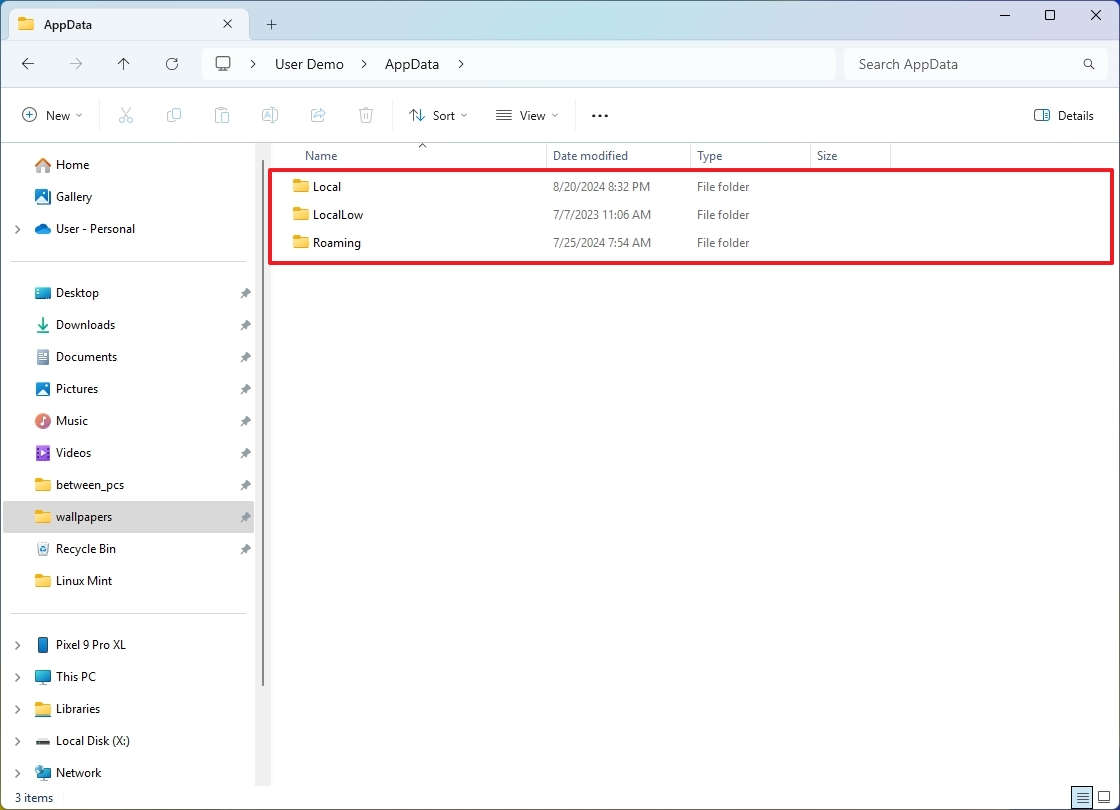
Inside the AppData folder, you will find three additional subfolders, including "Local," "LocalLow," and "Roaming."
(Image credit: Mauro Huculak)
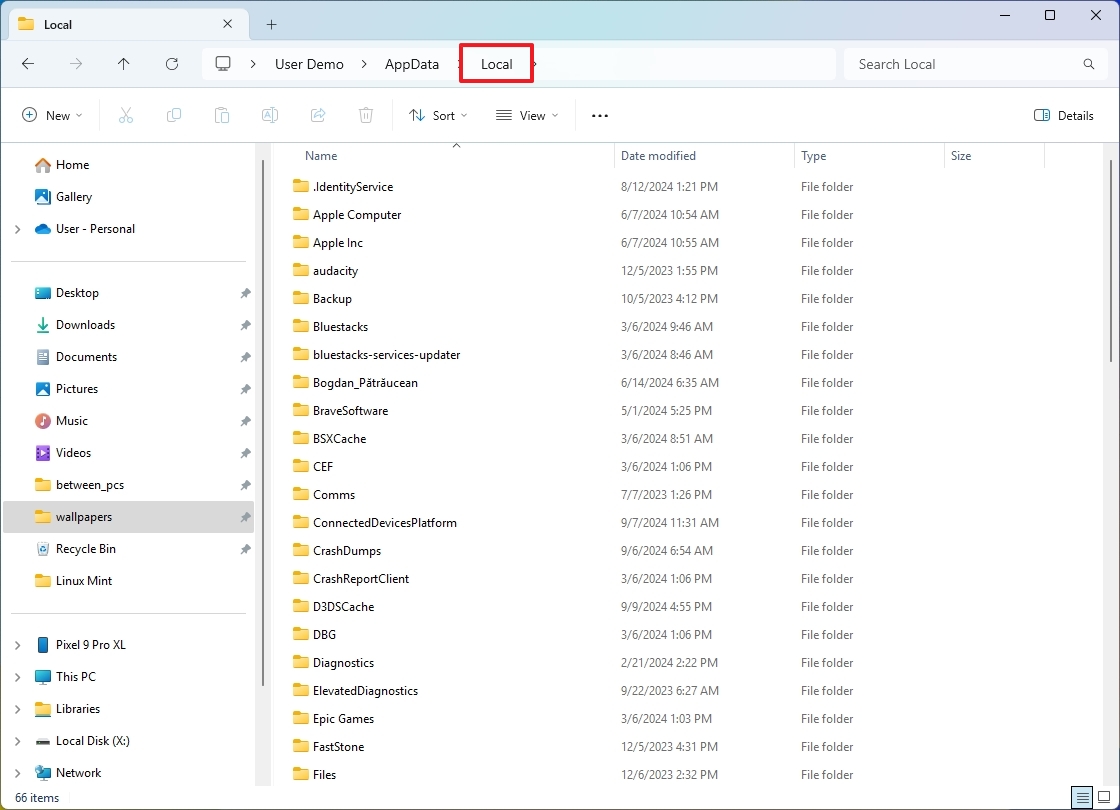
Local folder
The "Local" folder is where apps store data specific to the device that doesn't sync across computers.
(Image credit: Mauro Huculak)
Usually, in this folder, apps save their configuration file and preferences. For example, in the Local folder, you will find the "Microsoft" folder, which includes the data for Microsoft Edge, Office, OneDrive, Event Viewer, Teams, and more, depending on the apps installed on your computer.
If you delete the "Edge" folder, this action will reset the browser completely. In this particular case, some of the settings will be tied to your Microsoft account, so signing back into the browser will resync some of your settings.


3175x175(CURRENT).thumb.jpg.b05acc060982b36f5891ba728e6d953c.jpg)


Recommended Comments
There are no comments to display.
Join the conversation
You can post now and register later. If you have an account, sign in now to post with your account.
Note: Your post will require moderator approval before it will be visible.