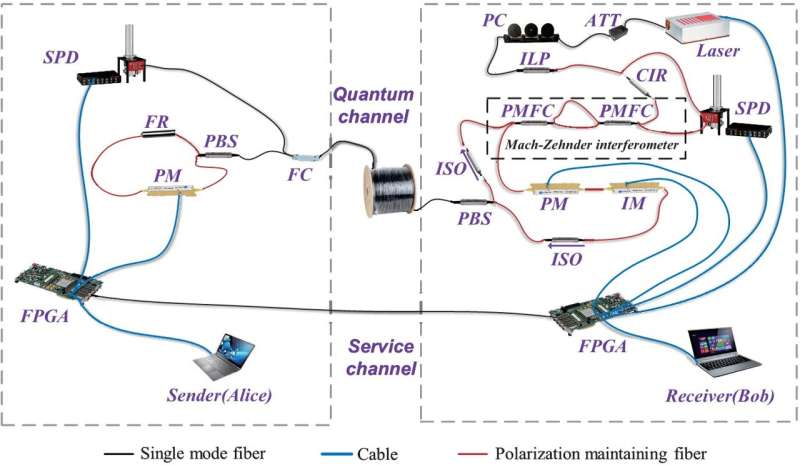
A team of researchers at Tsinghua University in China, has broken the distance record for quantum secure direct communication (QSDC) by sending information using their protocol a distance of 102.2 km. In their paper published in the journal Light: Science and Applications, the group describes how they devised a new QSDC protocol and used it to send secure signals over a fiber cable to extend the distance such messages could be sent.
QSDC takes advantage of entanglement as a means of securing network transmission over unsecured data lines. Because such particles are linked in a way that cannot be changed, protocols using them cannot be hacked without being detected by systems on the intended receiving end of such messages. As research has progressed to allow for the use of QSDC in real-world applications, the goal has been to reduce errors, increase transmission rates and, above all, extend the distance that messages using the protocol can be sent. Prior to this new effort, the record was just 18 km.
To extend that distance, the researchers devised a new QSDC protocol, one that involves the use of photonic time-bin states for monitoring signals and phase states for the actual communication messages. The researchers suggest adding such features to the QSDC protocol protects against phase errors and polarization. Further, it does not rely on feedback nor accurate matching of pairs of interferometers. They also suggest it makes such systems more reliable as well, which in turns leads to a lower error rate. And lowering the error-rate allows for extending the distance messages using the protocol can be sent.
The researchers acknowledge that the transmission rate is slow, at just 0.54 bps, which is slower even than systems using classical computing. But they note that it is still fast enough to allow for sending encrypted messages or even phone calls. They suggest their work shows that it is possible to create intercity QSDC-based networks using current technology. And they further suggest that certain parts of the Internet now in place could be replaced with parts based on the QSDC protocol they have developed to allow for hacker-resistant communications.
- Mutton
-

 1
1


Recommended Comments
There are no comments to display.
Join the conversation
You can post now and register later. If you have an account, sign in now to post with your account.
Note: Your post will require moderator approval before it will be visible.