Do you have to check how your drive is performing during specific tasks? Here are two ways on Windows 11.
On Windows 11, you can monitor the system drive activity, such as transfer rates and response time, to understand the performance of the storage at a given time, and in this guide, I will explain two ways to complete this task without third-party software.
Although most laptops and desktop computers have switched to Solid-State Drives (SSDs), which are a lot faster than traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), regardless of the storage technology, depending on the application and the task at hand, it will generate a number of reads and writes that can affect performance.
If you want to check the drive activity to understand the performance or if you have to troubleshoot storage-related issues on Windows 11, you can use the Task Manager and Performance Monitor to view transfer rates, response times, and other information in real-time.
In this how-to guide, I will explain the easy steps to check the drive activity on Windows 11. These instructions focus on two easy ways to check the drive performance at a given time. You can use these steps to test the drive performance, or I have also written another guide to help you determine the health of an SSD.
How to monitor drive activity from Task Manager
To check the drive activity through Task Manager, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Task Manager and click the top result to open the app.
- Click on Performance from the left pane.
- Select the drive from the left side.
- Check the "Active time" section to review the percentage of reads and writes over time (every 60 seconds).
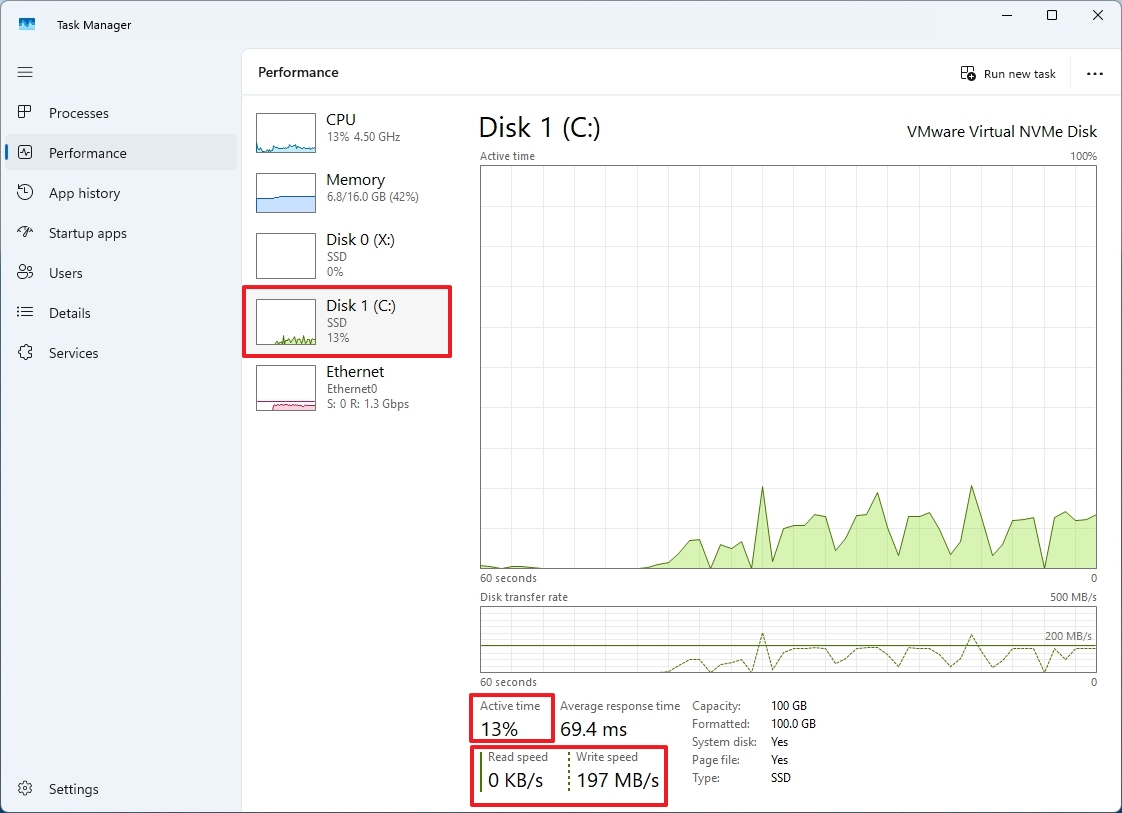
(Image credit: Mauro Huculak)
- Quick note: This information is also represented in the main "Active time" graph.
- Check the "Average response time" information, which is the amount of time it takes for a hard drive or solid-state drive to respond to a read or write request from the operating system.
- Check the "Read speed" and "Write speed" to determine the current speeds (Kilobytes or Megabytes per second) of the drive.
- Quick note: This information is also represented in the main "Disk transfer rate" graph.
Once you complete the steps, you will have an overview of the overall performance of the drive.
How to monitor drive activity from Performance Monitor
To monitor the drive activity with the legacy Performance Monitor app, use these steps:


3175x175(CURRENT).thumb.jpg.b05acc060982b36f5891ba728e6d953c.jpg)
Recommended Comments
There are no comments to display.
Join the conversation
You can post now and register later. If you have an account, sign in now to post with your account.
Note: Your post will require moderator approval before it will be visible.