Google released the weekly security update for its Chrome web browser a few hours ago. The update for Chrome Stable and Chrome Extended Stable fixes nine unique security issues in the browser. Since it is a point update, it does not introduce any non-security changes in the browser.
Chrome users may want to update the web browser as soon as possible. While Chrome supports automatic updates, these may take days or sometimes even weeks before they are pushed to all installations.
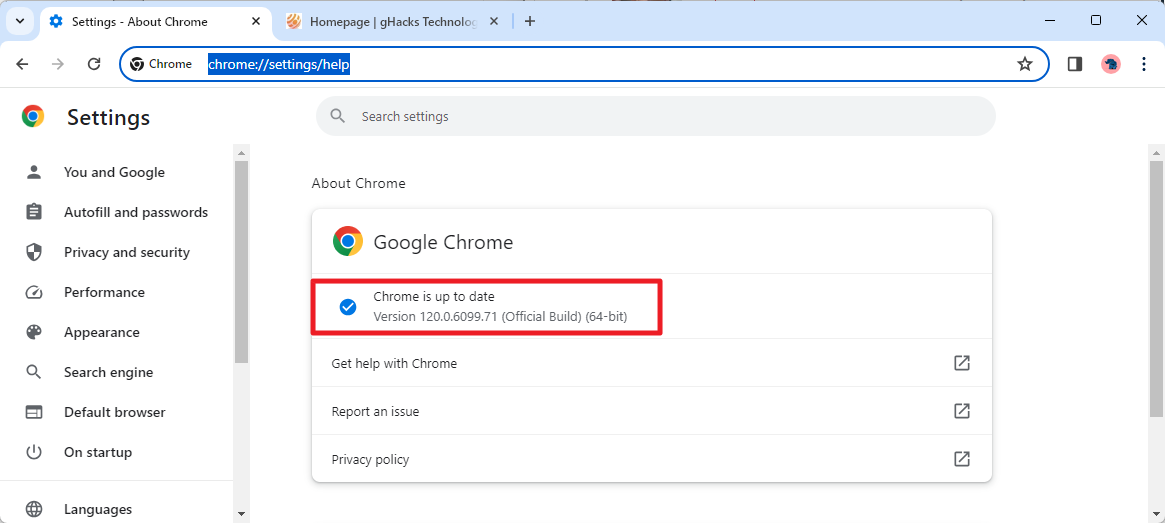
The best way to update immediately is to load chrome://settings/help in the browser's address bar. Chrome displays the version of the browser and checks for updates. If an update is found, it will be downloaded and installed automatically. A restart is required to complete the process.
The update is available for all desktop versions of Chrome as well as Chrome for Android. One of the following versions should be displayed after the successful update installation:
- Chrome for macOS, Linux or Windows: 120.0.6099.109
- Chrome Extended for macOS and Windows: 120.0.6099.109
Google released Chrome 120 Stable last week. Besides security fixes, Chrome 120 did introduce several non-security changes. Notable is the dropped support for Android 7 Nougat devices, a new proactive Safety Check feature, the sending of URL-based signals as part of the browser's Permission Suggestion Service, and the ability to share passwords to other members of a Family Group account.
Google Chrome 120
The Chrome security update patches nine security issues in the browser. Six of the nine security issues are listed on the official Chrome Releases website. The three undisclosed vulnerabilities were detected internally by Google. Google never reports internally discovered vulnerabilities publicly.
Here is the list of disclosed vulnerabilities:
- [$16000][1501326] High CVE-2023-6702: Type Confusion in V8. Reported by Zhiyi Zhang and Zhunki from Codesafe Team of Legendsec at Qi'anxin Group on 2023-11-10
- [$7000][1502102] High CVE-2023-6703: Use after free in Blink. Reported by Cassidy Kim(@cassidy6564) on 2023-11-14
- [$7000][1504792] High CVE-2023-6704: Use after free in libavif. Reported by Fudan University on 2023-11-23
- [$7000][1505708] High CVE-2023-6705: Use after free in WebRTC. Reported by Cassidy Kim(@cassidy6564) on 2023-11-28
- [$6000][1500921] High CVE-2023-6706: Use after free in FedCM. Reported by anonymous on 2023-11-09
- [$7000][1504036] Medium CVE-2023-6707: Use after free in CSS. Reported by @ginggilBesel on 2023-11-21
All but one have a severity rating of high, which is second only to critical in terms of severeness. Most patches address use after free vulnerabilities in various components, including WebRTC, libavif and CSS. There is a single type confusion in V8 issue listed as well.
Google makes no mentions of exploits in the wild. This means that the company is not aware of exploits that target the fixed vulnerabilities actively at the time. There is a possibility that exploits will be created after the release of the update, which is one reason for updating Chrome as soon as possible.
Now You: do you use Google Chrome?



3175x175(CURRENT).thumb.jpg.b05acc060982b36f5891ba728e6d953c.jpg)
Recommended Comments
There are no comments to display.
Join the conversation
You can post now and register later. If you have an account, sign in now to post with your account.
Note: Your post will require moderator approval before it will be visible.