Ukrainian Police Nab Six Tied to CLOP Ransomware
Authorities in Ukraine this week charged six people alleged to be part of the CLOP ransomware group, a cybercriminal gang said to have extorted more than half a billion dollars from victims. Some of CLOP’s victims this year alone include Stanford University Medical School, the University of California, and University of Maryland.
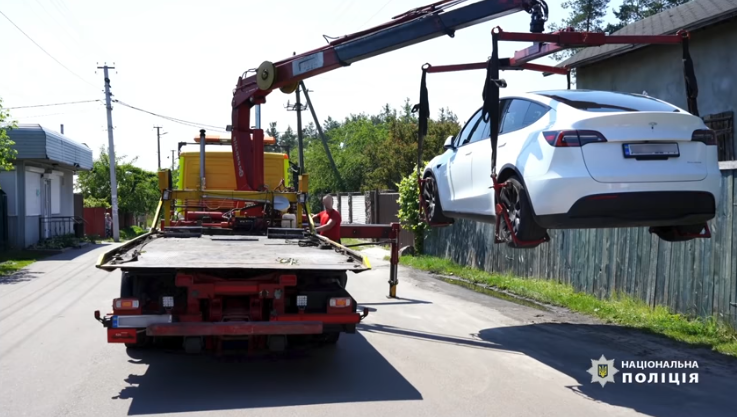

A still shot from a video showing Ukrainian police seizing a Tesla, one of many high-end vehicles seized in this week’s raids on the Clop gang.
According to a statement and videos released today, the Ukrainian Cyber Police charged six defendants with various computer crimes linked to the CLOP gang, and conducted 21 searches throughout the Kyiv region.
First debuting in early 2019, CLOP is one of several ransomware groups that hack into organizations, launch ransomware that encrypts files and servers, and then demand an extortion payment in return for a digital key needed to unlock access.
CLOP has been especially busy over the past six months exploiting four different zero-day vulnerabilities in File Transfer Appliance (FTA), a file sharing product made by California-based Accellion.
The CLOP gang seized on those flaws to deploy ransomware to a significant number of Accellion’s FTA customers, including U.S. grocery chain Krogers, the law firm Jones Day, security firm Qualys, and the Singaporean telecom giant Singtel.
Last year, CLOP adopted the practice of attempting to extract a second ransom demand from victims in exchange for a promise not to publish or sell any stolen data. Terabytes of documents and files stolen from victim organizations that have not paid a data ransom are now available for download from CLOP’s deep web site, including Stanford, UCLA and the University of Maryland.
CLOP’s victim shaming blog on the deep web.
It’s not clear how much this law enforcement operation by Ukrainian authorities will affect the overall operations of the CLOP group. Cybersecurity intelligence firm Intel 471 says the law enforcement raids in Ukraine were limited to the cash-out and money laundering side of CLOP’s business only.
“We do not believe that any core actors behind CLOP were apprehended, due to the fact that they are probably living in Russia,” Intel 471 concluded. “The overall impact to CLOP is expected to be minor although this law enforcement attention may result in the CLOP brand getting abandoned as we’ve recently seen with other ransomware groups like DarkSide and Babuk” [links added].
While CLOP as a moneymaking collective is fairly young organization, security experts say CLOP members hail from a group of Threat Actors (TA) known as “TA505,” which MITRE‘s ATT&CK database says is a financially motivated cybercrime group that has been active since at least 2014. “This group is known for frequently changing malware and driving global trends in criminal malware distribution,” MITRE assessed.
- aum
-

 1
1



3175x175(CURRENT).thumb.jpg.b05acc060982b36f5891ba728e6d953c.jpg)
Recommended Comments
There are no comments to display.
Join the conversation
You can post now and register later. If you have an account, sign in now to post with your account.
Note: Your post will require moderator approval before it will be visible.