Among the many items recovered from King Tut's tomb was a dagger made of iron, which is a material that was rarely used during Egypt's 18th dynasty. That iron likely came from a meteorite, and a recent paper published in the journal Meteorites and Planetary Science sheds further light on precisely how that iron dagger was forged, as well as how it came into Tut's possession.
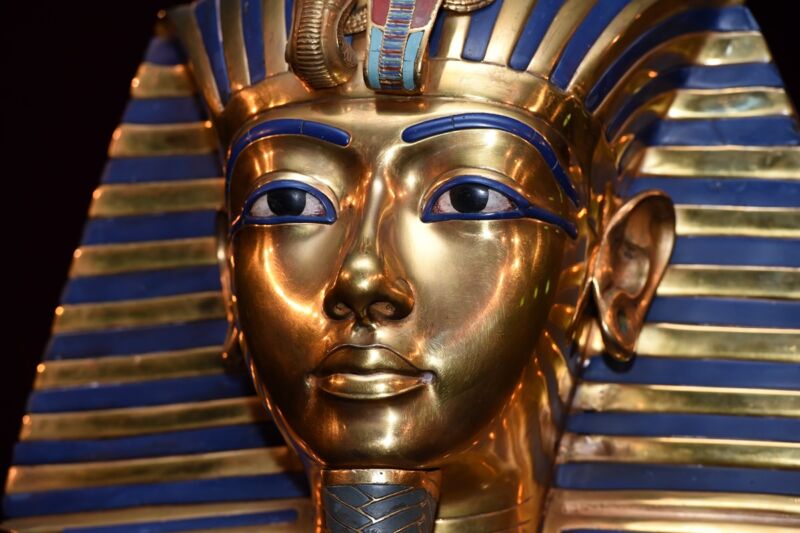
Tutankhamen was the son of Akhenaten and ascended to the throne when he was just 8 or 9 years old. He wasn't considered an especially important pharaoh in the grand scheme of things, but the treasures that were recovered from his tomb in the 1920s are what led to his fame. Those treasures included the famous gold burial mask (pictured above), a solid gold coffin, thrones, archery bows, trumpets, a lotus chalice, and various pieces of furniture.
These became part of a global touring exhibition, which received worldwide press coverage during the 1960s and 1970s in particular. The mummy even inspired a couple of songs: Steve Martin's hit "King Tut" (which debuted on Saturday Night Live in 1978) and the lesser-known "Dead Egyptian Blues," by the late folk rock singer Michael Peter Smith (which contains the immortal line, "Your sarcophagus is glowing, but your esophagus is showing").
CT scans of Tut's mummified remains in 2005 revealed that the young king had a deformed left foot and likely used a cane (several canes were found in the tomb). He also had a partially cleft hard palate and perhaps a mild case of scoliosis. The Egyptian Supreme Council of Antiquities and National Geographic commissioned a facial reconstruction of the boy king, which was ultimately cast in silicone. How he died remains a mystery: malarial infection, a nasty fall, and sickle cell anemia have all been proposed as possible cause of death. (Murder by blunt force trauma to the head was ruled out by the CT scan.)
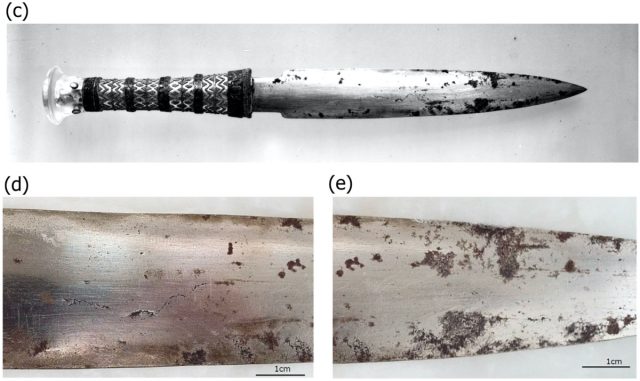
Among the more than 5,000 artifacts recovered from Tut's tomb were 19 objects made of iron, including the dagger with its golden hilt, a miniature headrest, an amulet, and a set of blades that may have been used for the "opening of the mouth" ceremony (performed so that the deceased could eat and drink in the afterlife).
There were also metallic beads and other precious stones strung across the mummy's waist and neck. Scientists analyzed one of the beads in 2013 and found that its microstructure and composition were very similar to that of an iron meteorite. The iron was likely worked into small thin sheets before being fashioned into beads. Archaeologists believe the use of iron was a means of indicating high status during this period in Egypt.
As for the dagger, its high nickel content led scientists to believe the iron for its blade likely came from a meteorite. This was confirmed in 2016, when the blade was subjected to X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (a nondestructive testing method) to analyze its composition. The blade turns out to be mostly iron, with 11 percent nickel and 0.6 percent cobalt—a composition that is indeed comparable to that of iron meteorites. By contrast, the nickel content of artifacts made from terrestrial iron ore is never higher than 4 percent.

However, that 2016 study didn't address the type of meteorite that supplied the iron or how the dagger might have been made. There is no archaeological evidence of iron smelting in Egypt until the 6th century BCE, and the earliest known example of Egyptian use of metallic iron dates to around 3400 BCE—before Egypt became a single state ruled by a pharaoh around 3000 BC. Options for the dagger's manufacture include cold working, which involves cutting and polishing an iron meteorite; hot working, in which the iron is melted at high temperature and subsequently cast; or low-temperature heating and subsequent forging.
The dagger's origin is also an open question. Unlike the other iron artifacts found in Tut's tomb, which were crudely fashioned, the dagger had been expertly made. There is written evidence of a foreign origin in diplomatic correspondence written in Akkadian from the Egyptian royal archives known as the Amarna letters (in the form of tablets). The letters mention a list of gifts sent to Amenhotep III by the king of Mitanni on the occasional of the former's marriage to a princess of Mitanni. The list includes a dagger with a blade of iron and a gold hilt with inlays of lapis lazuli.
It's those questions that co-author Takafumi Matsui and his colleagues at the Chiba Institute of Technology in Japan hoped to answer, with the help of the Grand Egyptian Museum's conservation center. They visited the Cairo Museum in February 2020.
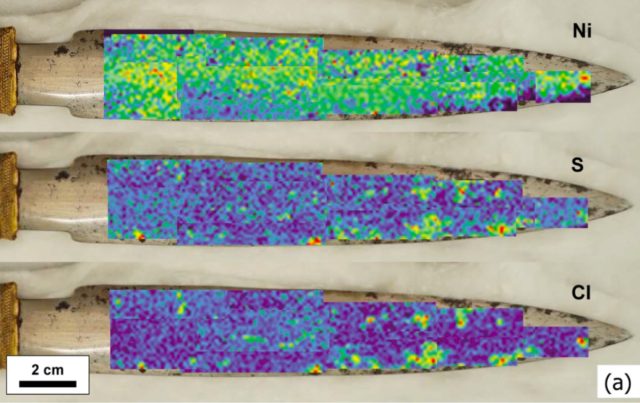
Matsui et al. took a high-resolution optical image of the dagger. They also used a portable scanning X-ray fluorescence instrument to measure the elemental abundances of the dagger, the gold hilt, and the gold sheath, as well as surveying how the elements were distributed across the blade. This revealed concentrations of iron, nickel, and cobalt (as measured in the 2016 study), as well as manganese. There were also several blackened spots on the blade, which contained sulfur, chlorine, calcium, and zinc.
It was the distribution of the elements on the blade that proved most interesting. They showed a distinct cross-hatched texture known as a "Widmanstätten pattern" (named after the Australian mineralogist Count Alois von Beckh Widmanstätten) that is typical of an octahedrite, the largest group of iron meteorites. This was confirmed when they compared the pattern on the dagger with that of a Japanese meteorite of the same type. The small black patches of iron sulfide are also found as inclusions in octahedrites.

According to the authors, the low amount of sulfur in the black patches and the Widmanstätten pattern comprised strong evidence that King Tut's dagger was forged at a relatively low heat of less than 950° C (1,724° F).
As for where the dagger came from, the Amarna letters offered a strong clue that it was a wedding gift to Amenhotep III by the king of Mitanni. This was bolstered by the fact that team found the gemstones in the gold hilt had been attached with lime plaster. Although lime plaster was commonly used in Mitanni at the time, Egyptians preferred to use gypsum plaster.
DOI: Meteorites and Planetary Science, 2022. 10.1111/maps.13787 (About DOIs).



3175x175(CURRENT).thumb.jpg.b05acc060982b36f5891ba728e6d953c.jpg)

Recommended Comments
There are no comments to display.
Join the conversation
You can post now and register later. If you have an account, sign in now to post with your account.
Note: Your post will require moderator approval before it will be visible.