A team of researchers from Germany, France and the U.K. has discovered a long thin filament of dense gas connecting two of the Milky Way galaxy's spiral arms. In their paper published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, the group describes their work studying carbon monoxide gas in the galaxy.
Prior research has shown that other galaxies have features called feathers—long gas filaments with barbs that look from Earth like feathers. But because it is very difficult to study the Milky Way galaxy from an Earth perspective, no such features have been seen, until now.
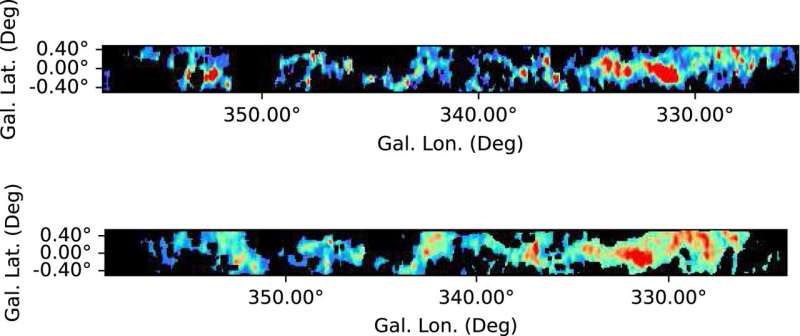
In their work, the researchers were studying concentrations of carbon monoxide gas in data from the APEX telescope in San Pedro de Atacama, Chile. They noticed concentrations that had not been seen before, and after taking a closer look, discovered that it was part of a large gas formation that extended from near the center of the galaxy outward, connecting two of the arms that give the galaxy its distinctive look.
The researchers named the formation the Gangotri wave—an homage to the massive glacier whose melting gives rise to the Ganges River. In India, the Milky Way galaxy is known as Akasha Ganga. The newly discovered feather spans approximately 5.6764e+16 to 1.22989e+17 kilometers in reaching between the two arms and is approximately 1.6083242e+17 kilometers from the rotational center of the galaxy. They have also estimated its mass to be approximately equal to nine million suns. Prior to the new discovery, all of the gas tendrils found in the Milky Way have aligned with the spiral arms.
The researchers found that the Gangotri wave has another unique and interesting feature in that it is not as straight as expected. Instead, it zig-zags back and forth along its length in a pattern similar to a sine wave. The researchers were not able to explain the strange phenomenon but note that some force must be at play—a force that is likely to be the focus of many upcoming research efforts. The team plans to continue their study of gases in the Milky Way, this time actively looking for new feathers.



Recommended Comments
There are no comments to display.
Join the conversation
You can post now and register later. If you have an account, sign in now to post with your account.
Note: Your post will require moderator approval before it will be visible.