For many people, the aroma of freshly brewed coffee is the start of a great day. But caffeine can cause headaches and jitters in others. That’s why many people reach for a decaffeinated cup instead.
I’m a chemistry professor who has taught lectures on why chemicals dissolve in some liquids but not in others. The processes of decaffeination offer great real-life examples of these chemistry concepts. Even the best decaffeination method, however, does not remove all of the caffeine—about 7 milligrams of caffeine usually remain in an 8-ounce cup.
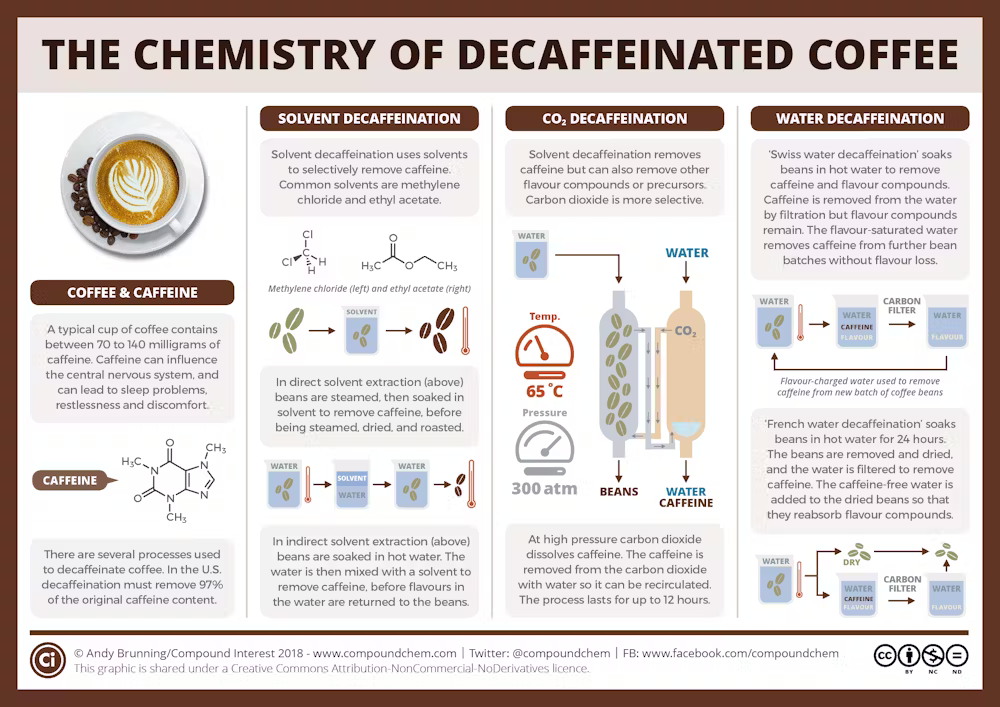
Producers decaffeinating their coffee want to remove the caffeine while retaining all—or at least most—of the other chemical aroma and flavor compounds. Decaffeination has a rich history, and now almost all coffee producers use one of three common methods.
All these methods, which are also used to make decaffeinated tea, start with green, or unroasted, coffee beans that have been premoistened. Using roasted coffee beans would result in a coffee with a very different aroma and taste because the decaffeination steps would remove some flavor and odor compounds produced during roasting.
The carbon dioxide method
In the relatively new carbon dioxide method, developed in the early 1970s, producers use high-pressure CO₂ to extract caffeine from moistened coffee beans. They pump the CO₂ into a sealed vessel containing the moistened coffee beans, and the caffeine molecules dissolve in the CO₂.
Once the caffeine-laden CO₂ is separated from the beans, producers pass the CO₂ mixture either through a container of water or over a bed of activated carbon. Activated carbon is carbon that’s been heated up to high temperatures and exposed to steam and oxygen, which creates pores in the carbon. This step filters out the caffeine, and most likely other chemical compounds, some of which affect the flavor of the coffee.
These compounds either bind in the pores of the activated carbon or they stay in the water. Producers dry the decaffeinated beans using heat. Under the heat, any remaining CO₂ evaporates. Producers can then repressurize and reuse the same CO₂.
This method removes 96 to 98 percent of the caffeine, and the resulting coffee has only minimal CO₂ residue.
This method, which requires expensive equipment for making and handling the CO₂, is extensively used to decaffeinate commercial-grade, or supermarket, coffees.
Swiss water process
The Swiss water method, initially used commercially in the early 1980s, uses hot water to decaffeinate coffee.
Initially, producers soak a batch of green coffee beans in hot water, which extracts both the caffeine and other chemical compounds from the beans.
It’s kind of like what happens when you brew roasted coffee beans—you place dark beans in clear water, and the chemicals that cause the coffee’s dark color leach out of the beans into the water. In a similar way, the hot water pulls the caffeine from not yet decaffeinated beans.
During the soaking, the caffeine concentration is higher in the coffee beans than in the water, so the caffeine moves into the water from the beans. Producers then take the beans out of the water and placed them into fresh water, which has no caffeine in it—so the process repeats, and more caffeine moves out of the beans and into the water. The producers repeat this process, up to 10 times, until there’s hardly any caffeine left in the beans.
The resulting water, which now contains the caffeine and any flavor compounds that dissolved out from the beans, gets passed through activated charcoal filters. These trap caffeine and other similarly sized chemical compounds, such as sugars and organic compounds called polyamines, while allowing most of the other chemical compounds to remain in the filtered water.
Producers then use the filtered water—saturated with flavor but devoid of most of the caffeine—to soak a new batch of coffee beans. This step lets the flavor compounds lost during the soaking process reenter the beans.
The Swiss water process is prized for its chemical-free approach and its ability to preserve most of the coffee’s natural flavor. This method has been shown to remove 94 to 96 percent of the caffeine.



3175x175(CURRENT).thumb.jpg.b05acc060982b36f5891ba728e6d953c.jpg)

Recommended Comments
There are no comments to display.
Join the conversation
You can post now and register later. If you have an account, sign in now to post with your account.
Note: Your post will require moderator approval before it will be visible.