Following at least two major blocking blunders at Italy's Piracy Shield system that were initially denied, it was hoped that authorities would take the opportunity to be more transparent. While that has failed to emerge, live data from the Piracy Shield platform is now being made available via an unofficial third-party service. That has revealed yet more blocking blunders, this time involving Akamai IPs.
After initially denying that Italy’s new Piracy Shield anti-piracy platform had been responsible for any over-blocking, last week telecoms regulator AGCOM conceded that an IP address belonging to Cloudflare had been blocked in error.
While that might be considered progress of sorts, the incident was downplayed as minor on the basis it was rectified a few hours later. No consolation for the many Cloudflare customers affected, of course, but that particular problem isn’t going away. Cloudflare is encouraging its customers to file complaints to draw attention to the perils of widespread blocking measures.
Yet despite calls for more transparency, not to mention an obvious need, AGCOM is still not reporting the IP addresses subjected to blocking, instead preferring to report the volume of IP addresses blocked instead. While the latter is not unimportant information, only the former can shine light on cases where IP addresses are blocked in error. Or when IP addresses are blocked despite the legal provision that prohibits blocking when IPs are not exclusively used for piracy.
New Third-Party Service Imposes Transparency
Official providers of all types of content have understood for some time that if they don’t meet demand, someone else will do it for them. After calls for transparency appeared to fall on deaf ears, transparency has been imposed on the Piracy Shield system thanks to a new, unofficial third-party system: Piracy Shield Search.
The most important feature of the service is the ability to enter an IP address or a fully qualified domain name (FQDN) to find out whether they’re on the Piracy Shield system.
The image below consists of an original blocking order (translated from Italian) issued in response to a blocking application by Sky Italia. To protect Sky’s broadcasting rights for FIM MotoGP World Championship and the Motul FIM Superbike World Championship, the domain http://live.vitocatozzo.eu was added to the Piracy Shield system.

The response from Piracy Shield Search added by us directly underneath the relevant section in the application confirms that the domain was indeed placed on the blocklist. The response also provides the time the rightsholder or its representative added the ticket to the system, which acts as the instruction for ISPs to go ahead and start blocking.
Rightsholder Tickets and Top AS By IP Address
The Piracy Shield Search system shows data relating to currently active blocking, not the total number of requests made or IP addresses/domains blocked to date.
In the image below we can see that 662 rightsholder tickets are currently live, and together they target 2,849 IPv4 IP addresses, zero IPv6 IP addresses, and 6,601 fully qualified domain names. The panel on the right shows the top AS (autonomous systems) ranked by the total number of IP addresses allocated to the AS that are currently subject to blocking.
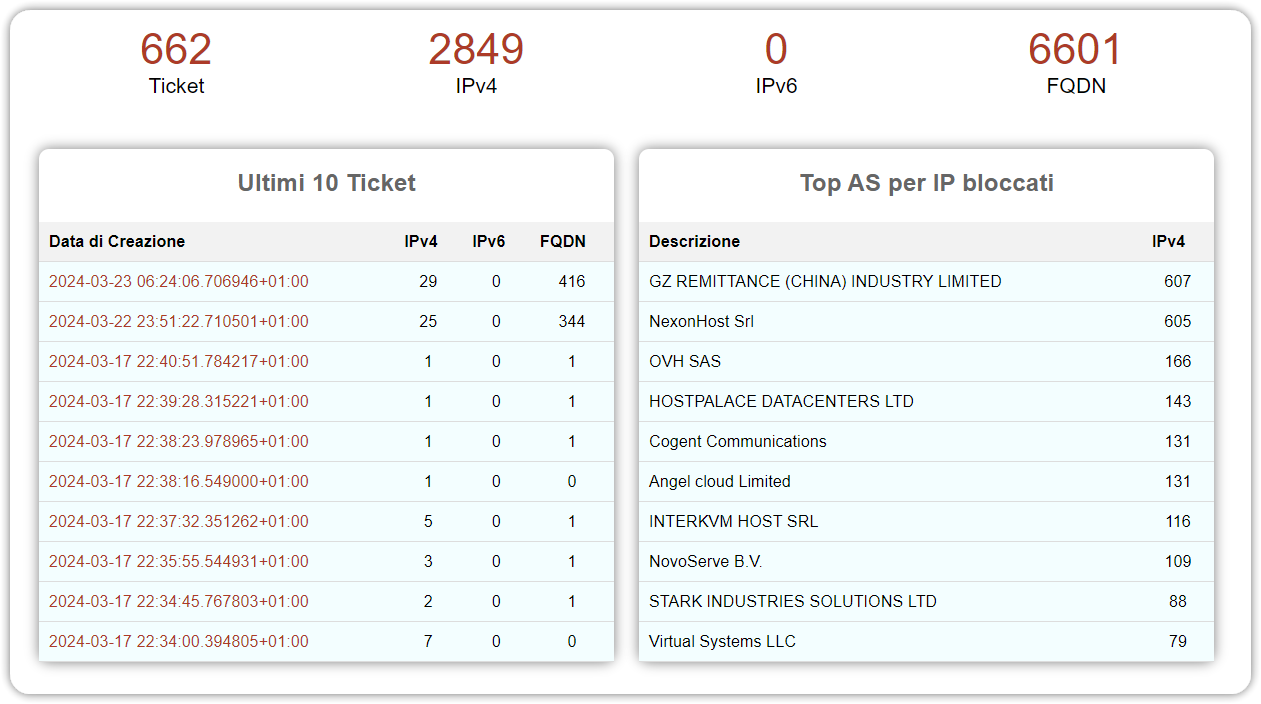
The ticket panel on the left shows that the system deployed in Italy operates similarly to the blocking system operated in the UK.
Much is made in the media about the requirement to block IP addresses and domains within 30 minutes, possibly to imply that blocking takes place mostly during live matches. However, the two items at the top of the list show that IP addresses and domains are typically added in bulk, long after matches finish or, alternatively, long before they actually start.
Tickets Reveal More Blocking Blunders
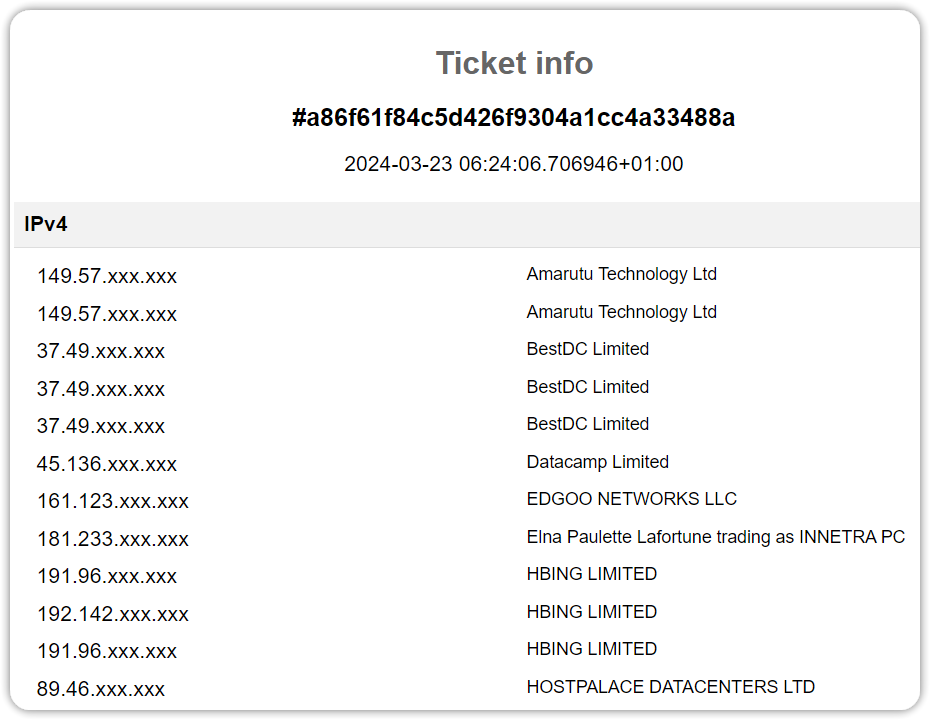
The people behind Piracy Shield Search have decided to partially redact IP addresses requested for blocking in rightsholder tickets. Since the search facility on the front page responds to requests for specific IP addresses, there’s no need to expose the IP addresses in full here.
However, since the names of the hosts are displayed in full, it’s possible to determine whether the IP addresses that appear on the left are likely to be operated by CDN companies. More importantly, there may also be enough information to determine whether multiple services potentially share the IP address.
In a post to X, developer and researcher Matteo Contrini confirms what many people had suspected; Cloudflare isn’t the only major CDN provider whose IP addresses have ended up on the Piracy Shield system.
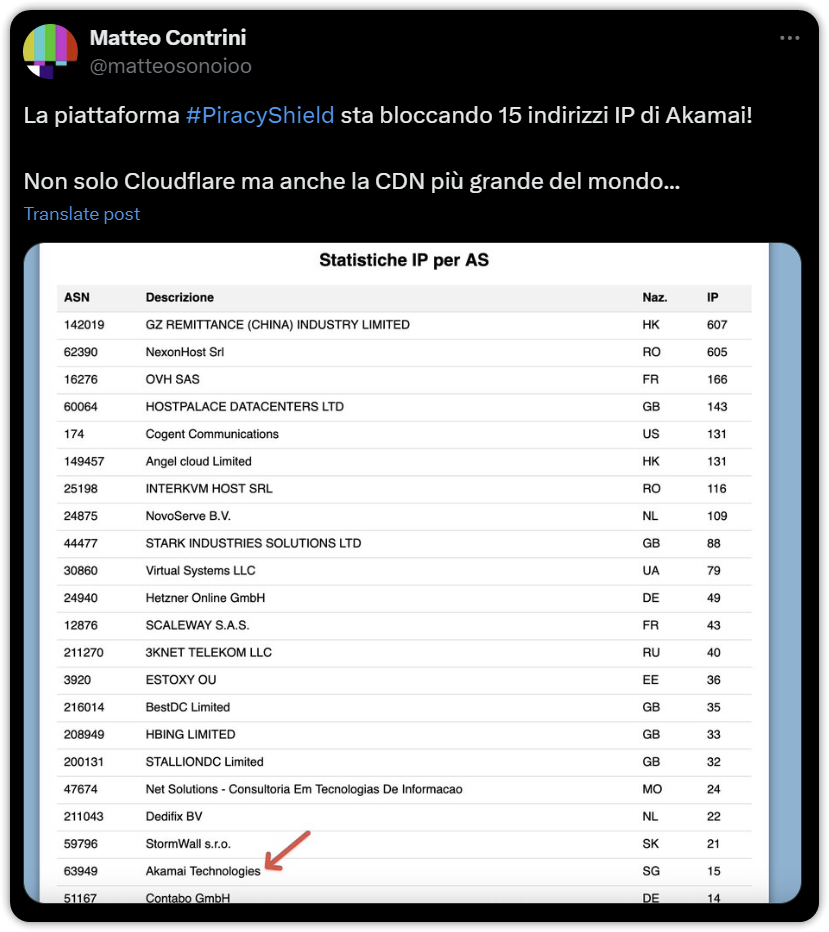
“The platform #PiracyShield is blocking 15 Akamai IP addresses! Not only Cloudflare but also the largest CDN in the world…,” Contrini notes.
The data suggests that transparency is a double-edged sword. Without transparency, there’s no scrutiny, and no specific fuel for criticism. When transparency exists, whether voluntarily or by imposition, scrutiny ensures that criticism can be backed up by data provided by the system itself.
What transparency offers that opacity never does, however, is a powerful incentive to do better. Whether the addition of these IP addresses is due to blunder after uncorrected blunder isn’t clear, but the alternative is unquestionably much worse.



3175x175(CURRENT).thumb.jpg.b05acc060982b36f5891ba728e6d953c.jpg)

Recommended Comments
There are no comments to display.
Join the conversation
You can post now and register later. If you have an account, sign in now to post with your account.
Note: Your post will require moderator approval before it will be visible.